House Edge in Baccarat: How the Casino Advantage Is Built In
Baccarat’s house edge is created by probability and payout design, not player behavior. This article explains how the casino advantage is mathematically embedded in the game.
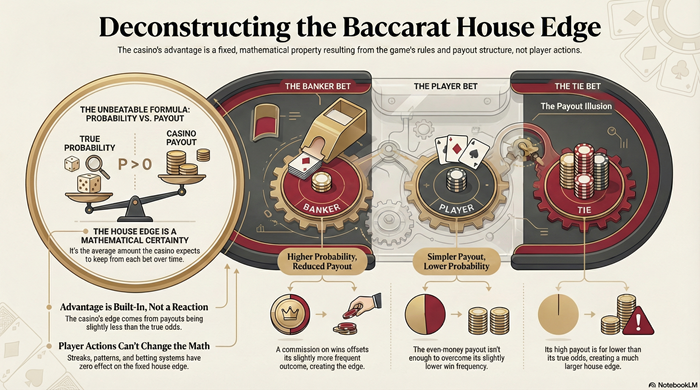
Baccarat’s house edge is created by probability and payout design, not player behavior. This article explains how the casino advantage is mathematically embedded in the game.
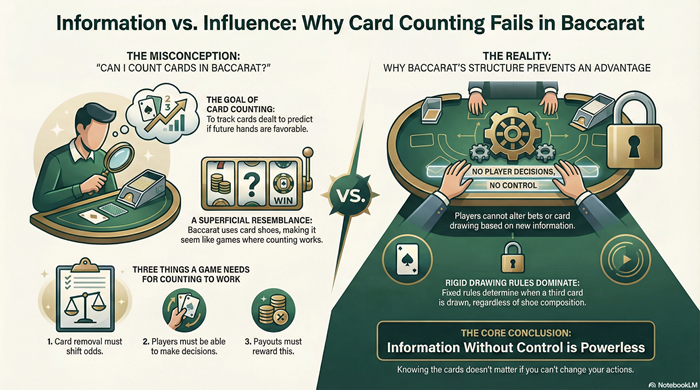
Card counting does not provide a functional advantage in baccarat. This article explains why shoe composition changes cannot be exploited, how fixed drawing rules block decision-based leverage, and why counting fails to alter probability or house edge. It focuses on game structure and mathematics, not betting methods.
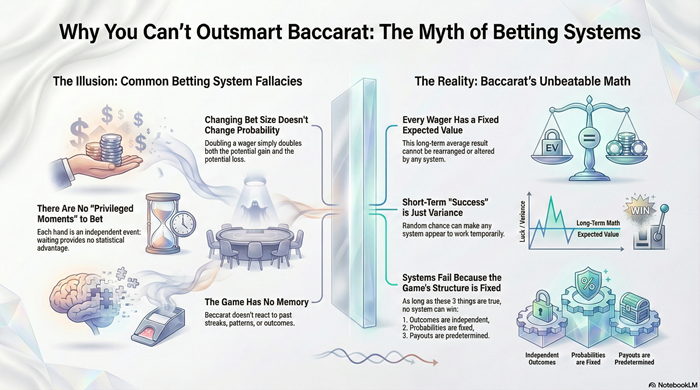
Betting systems rearrange variance without changing probability. This article explains, at a structural level, why no system can overcome baccarat’s fixed expectation.
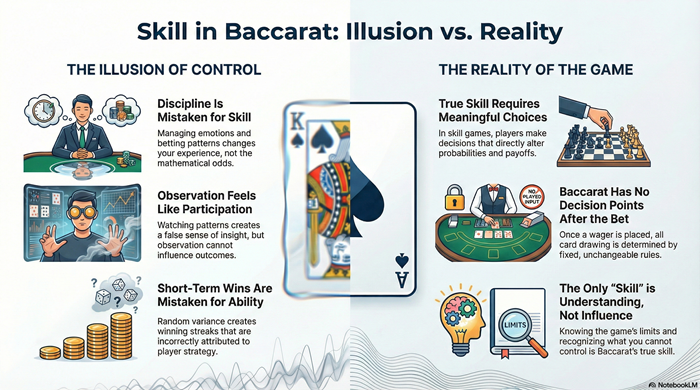
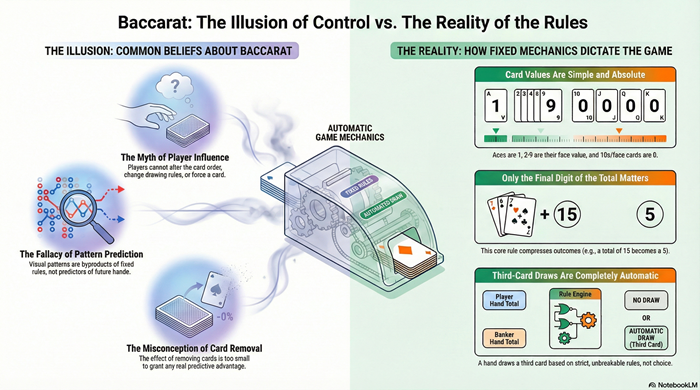
Skill in baccarat is often misunderstood. This article explains why player ability cannot influence outcomes, how discipline differs from skill, and why understanding the game improves interpretation but not probability. It focuses on structural limits and perception, not wagering advice or strategies.
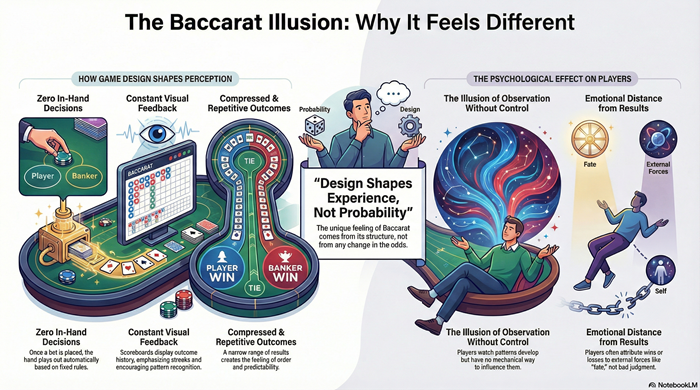
Baccarat feels different from other casino games because it removes player decisions, compresses outcomes, and emphasizes continuous visual feedback. This article explains how design and presentation shape perception, why observation replaces control, and why the experience feels structured even though probability remains unchanged.
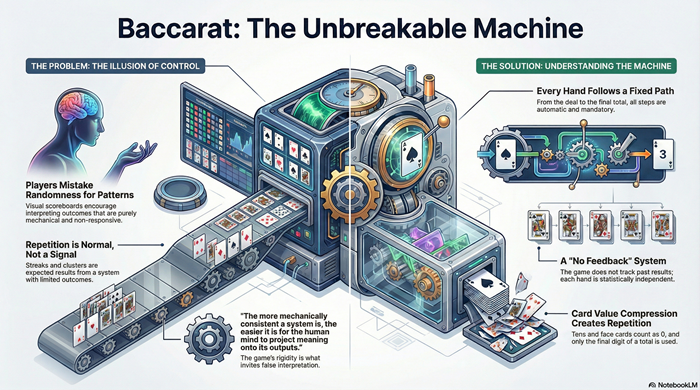
Baccarat outcomes are produced through rigid drawing rules and compressed card values. This article explains how repetition, clustering, and apparent structure arise naturally from the game’s mechanics rather than from hidden signals.
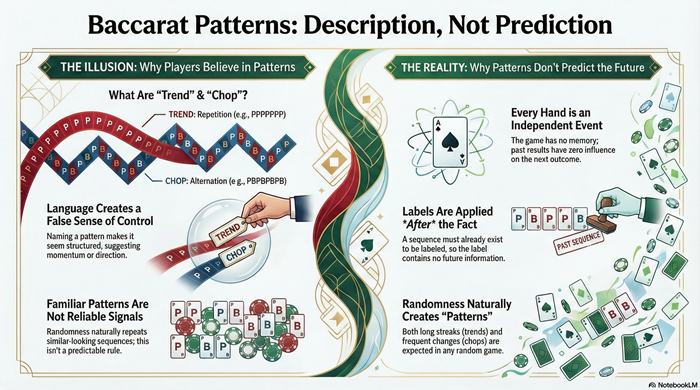
“Trend” and “chop” in baccarat are labels applied to past outcome sequences, not indicators of future probability. This article explains why random sequences naturally produce repetition and alternation, how language creates the illusion of structure, and why these terms do not carry predictive value. It focuses on probability and interpretation, not betting behavior.
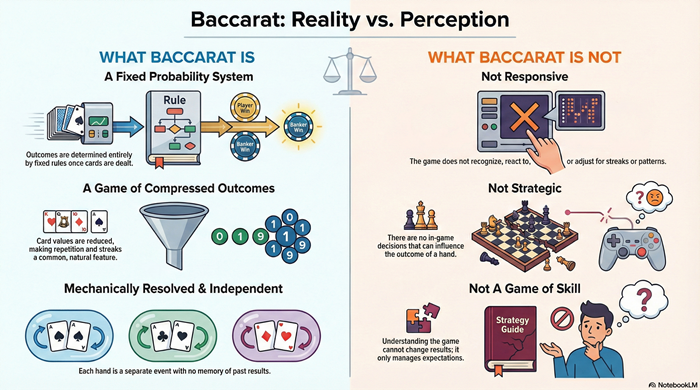
Baccarat is a mechanically resolved card game governed by fixed rules and stable probabilities. This article explains what baccarat fundamentally is—and why beliefs about influence, timing, and interpretation misunderstand how the game actually functions.
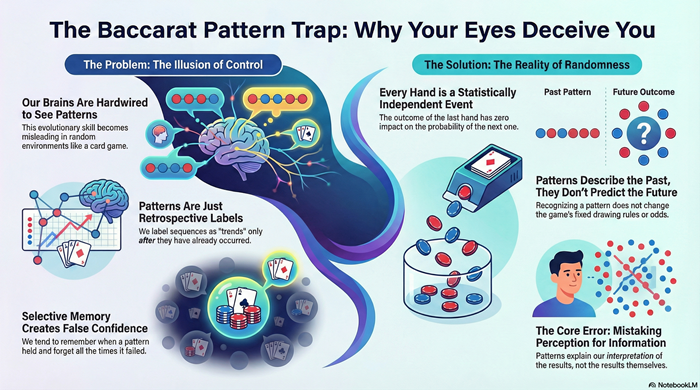
Pattern recognition in baccarat reflects human perception, not predictive information. This article explains why random sequences naturally appear structured, how cognitive bias reinforces false confidence, and why identifying patterns does not change probability or outcomes. It focuses on mathematics and perception, not wagering strategies.
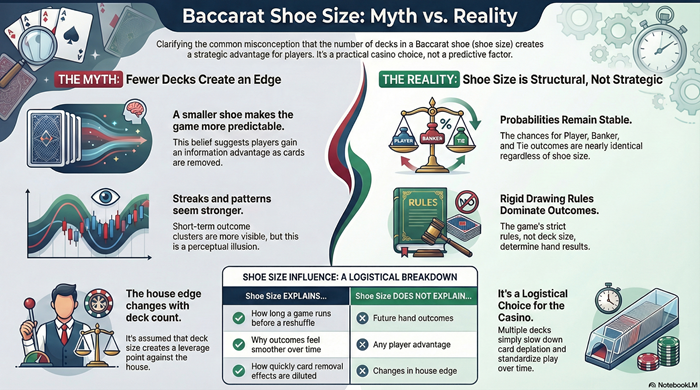
Shoe size in baccarat refers to the number of decks used, not a source of advantage. This article explains why multiple decks are used, how card removal affects distribution, and why changing shoe size does not alter probability or house edge. It focuses on game structure and mathematics, not betting behavior or strategy.

The Tie outcome in baccarat exists because the game’s card values and drawing rules make equal hand totals unavoidable. This article explains why the Tie is a structural necessity, how it fits into the game’s design, and why it does not affect the probability of other outcomes. It focuses on game mechanics, not wagering advice.
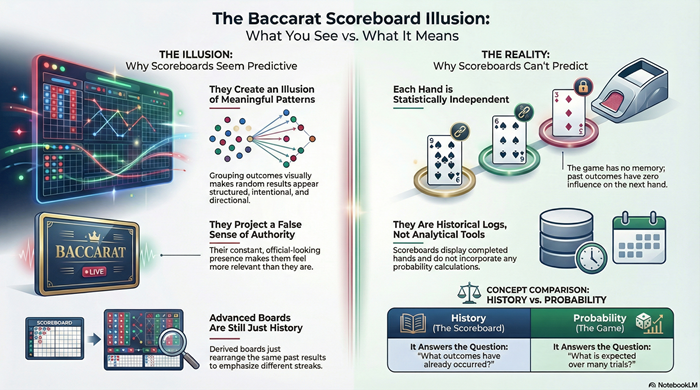
Baccarat scoreboards display past outcomes, not future probability. This article explains how different scoreboard formats visually organize history, why those displays encourage pattern interpretation, and why recorded results do not influence upcoming hands. It focuses on probability and perception, not betting methods or strategy.
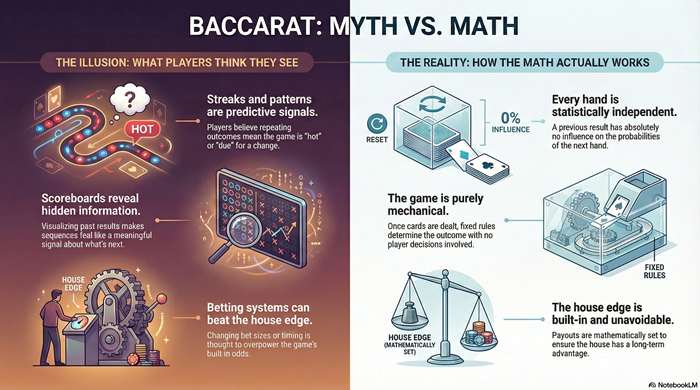
Baccarat is a fixed-rule card game governed by stable probabilities and a built-in house edge. This guide explains how baccarat outcomes are produced, what odds actually describe, why streaks and patterns appear, and why betting systems fail mathematically. It focuses on structure, independence, and expectation—clarifying what baccarat can explain and what it never changes.
The house edge in baccarat is a fixed mathematical property created by the game’s rules and payout structure. This article explains what house edge actually measures, why it applies consistently over time, and why betting systems and wager timing cannot change expected outcomes. It focuses on probability, not strategy or advice.
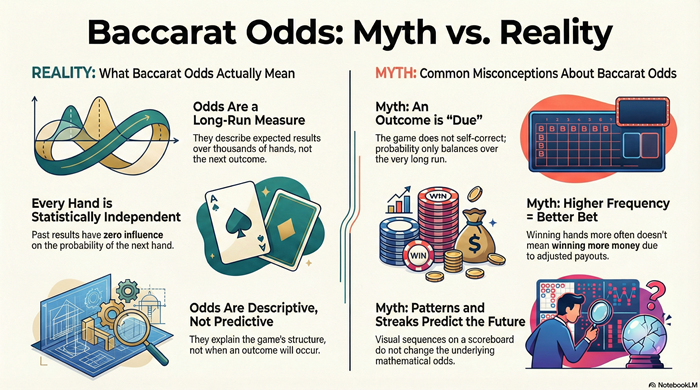
Baccarat odds describe how outcomes are expected to occur over a very large number of hands, not what will happen next. This article explains what odds actually measure, why short-term results are misleading, and why higher hit frequency does not imply better value. It focuses on probability and structure, not betting advice or strategy.